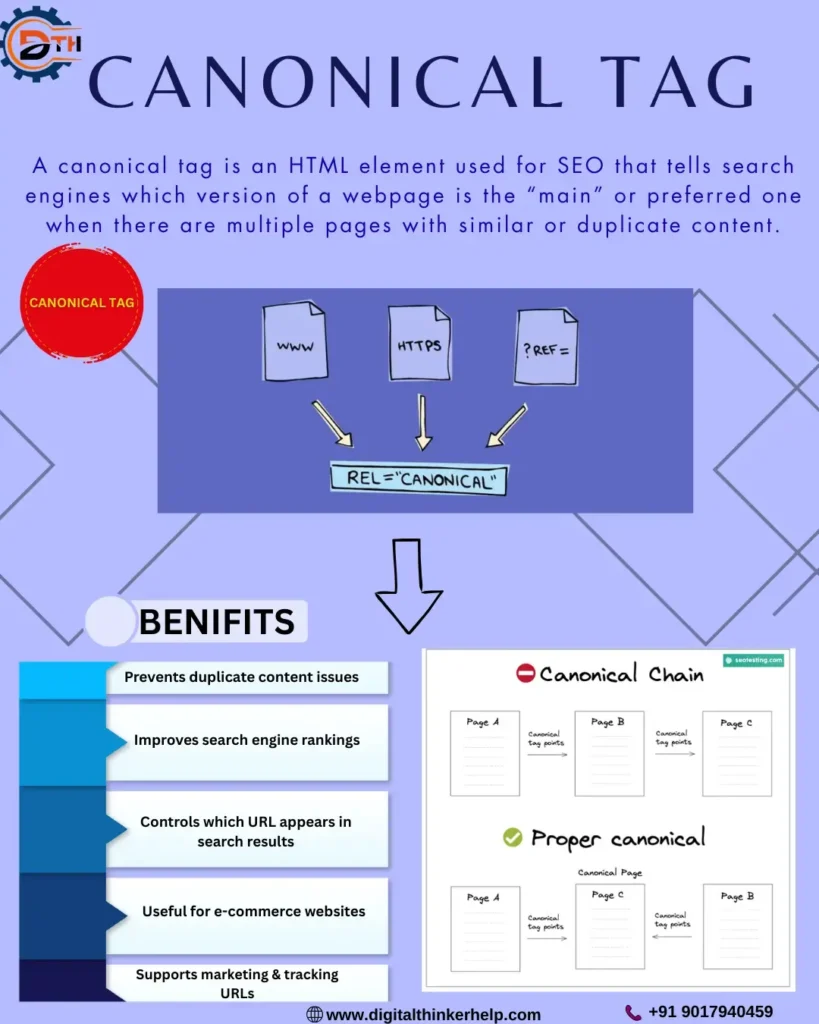
Canonical Tag means canonicalization possibly sound complex, but it is actually a simple idea. It helps search engines know which page on your website must be treated as the main or favorite one when few pages have similar content.
This is done between canonical tags, which tell search engines the master or first version of a page.
In this guide, you will learn everything you need to know around canonical URLs and canonical tags. We will explain how they work and how you capable of add canonical tags easily without any technical difficulty.
What is a Canonical Tag in SEO?
A canonical tag (or rel=”canonical”) is a part of code set inside the <head> section of a webpage. It tells search engines which URL is the important or choose version of a page.
Canonical tags help avoid problems when the same or very similar content looks on multiple pages of your website.
In simple words, we use canonical tags to guide search engines to the correct page types so it look in search results, and to stop duplicate content issues.
Importance of Canonical Tags in SEO
Canonical tags help search engines show which pages them very good index and show in search results.
Also Read: What are Generic Keywords with Example? Branded vs Generic Keywords
If you do not set a canonical tag, search engines purpose picks the page they believe is the main one. This is not important because their choice may not match the page you actually want to rank.
When you have many alike pages, it capable of also waste your crawl budget. This means search engines may spend time crawling duplicate pages by choice of finding new or important content on you.
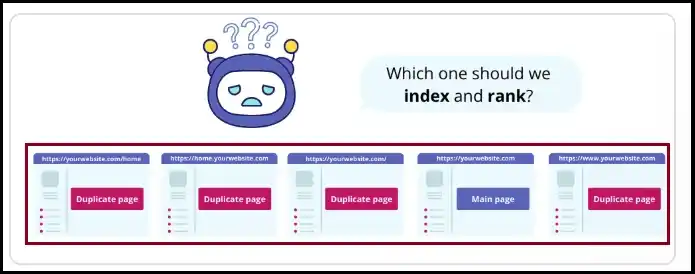
When the same page looks under different URLs, people may link to different versions by choice of one correct URL. As a result, the link value does not go to the main page where it must.
This shows how important canonical tags are. Ignoring them capable of create big SEO problems.
Canonical tags help search engines index and rank the correct page. They also combine all link value into the main version and help save your crawl budget.
But canonical tags work successfully only when you use them correctly and follow best practices.
Why do Canonical Tags Matter for SEO?
Google’s John Mueller explains it clearly: using a self suggestive canonical tag helps Google understand which page you want indexed and which URL must look in search results.
This is exactly why canonical tags are important. They show search engines the correct, main version of a page and stop your own pages alike competing with each other.
Canonical tags matter because they provide several important benefits:
They prevent duplicate content problems. Canonical tags tell Google which URL must be indexed so similar or duplicate pages do not confuse search engines or weaken your rankings.
They combine link equity. Instead of spreading ranking power across different versions of the same page, canonicalization sends all that power to one main URL.
They improve crawl efficiency. Search engines avoid wasting time on duplicate pages and capable of focus on discovering new, important content on your website.
They improve user experience. Visitors are sent to the correct and updated page, not a duplicate version created by filters, parameters, or other variations.
When to Use Canonical Tag?
You must use a canonical tag whenever the same or very similar content looks on more than one URL. Under is the most common case where canonical tags are needed.
Your homepage capable of read between many URLs, like www.domain.com,domain.com, or www.domain.com/index.html.
Also Read: What are Transactional Keywords in SEO? Example & How to Find Them
A page possibly loads with or without a trailing slash (/) or with different letter cases, but still shows the same content.
Due to URL rewriting, the server may treat many URL versions as the same page, even between the addresses look different.
Some URLs include IDs like session IDs or product filter IDs, but the page content remains unchanged.
The same content is available in multiple formats, such as a daily web page, a print version, or a PDF file.
There are HTTPS versions of your site that display the same content.
The same page might still be ready between older HTTP versions without SSL security.
Your content might also looks on external websites, creating multiple versions of the same page.
How to Add Canonical Tags to Your Website?
They are the different path to add canonical tags:
Add canonical tag in word press without plug-in – Manually
You capable of add a canonical tag manually by placing <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com”/> inside the <head> section of your page’s code. However, most people do not do it this way because it takes time and able to be difficult. Instead, it’s much easy to set up canonical tags directly between your website platform or CMS.
Add Canonical Tag in Word Press
You can set canonical URLs on your Word Press website by using an SEO plug-in.
Also Read: What are Navigational Keywords in SEO? Examples & How to Find Them
Here are simple orders like adding canonical URLs with two of the most popular plugging: Yoast SEO and Rank Math SEO.
Add Canonical Tag in Word Press SEO Plugin –
Yoast Plugin
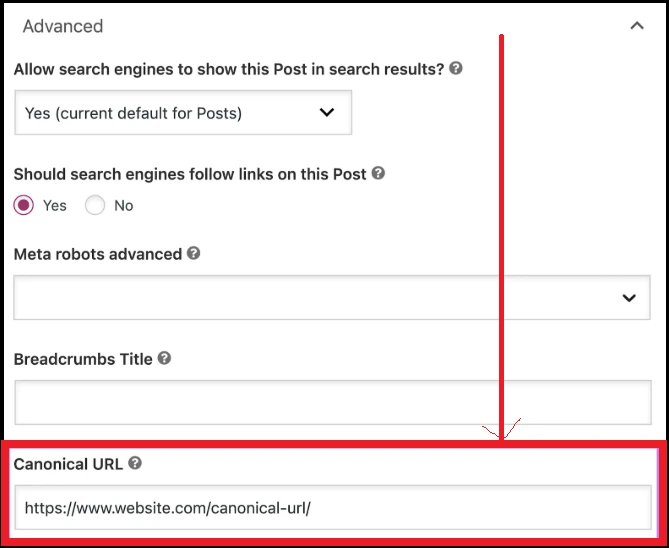
To add a canonical URL like the Yoast SEO plugin, open the Yoast SEO settings spot on the page or post you are editing.
Then click on the “Advanced” tab to view more choice.
In the “Canonical URL” box, enter the URL you like to set as the main type of the page.
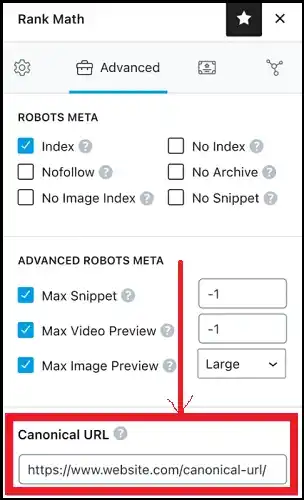
Rank Math SEO Plugin
To set a canonical URL like the Rank Math SEO plugin, open the “Rank Math SEO” panel on the page or post you are editing and click on the “Advanced” tab.
Then, type the select canonical URL into the “Canonical URL” field.
Can Google Ignore Canonical Tags?
It is known to understand that canonical tags act as advice like Google. They guide Google, but Google does not have to follow them.
If Google’s systems believe another page is a better choice like the canonical version, they may select that page instead.
To know how Google decides, here is what they explain:
When Google finds few pages with the same or very similar content, it chooses the one that looks to be the most complete, helpful, and to the point like users. That page is then decided as the canonical version.
Google considers few part when choosing a canonical page, they involve:
Whether the page URL is involve in your sitemap. This is a weak signal.
Whether you have added a canonical tag to the page, this is a strong signal.
Implement Canonicals with 301 Redirects
Redirects are a great way to remove duplicate of your pages without actually removes any URLs. Google suggest using 301 or 302 server side redirects to set the correct canonical version.
A 301 redirect is usually the good choice because it is permanent and clear informs search engines which page must be use as the main one.
The steps to create a 301 redirect depend are your CMS, but most platforms build it easy. You will easily find a loyal redirects section where you simply enter the old URL and the new stop URL.
Also Read: What Are Commercial Keywords in SEO? Examples & How to Find Them
Redirects are mainly helpful if you are restructuring many URLs or improve how your internal links work.
With redirects, both users and search engines are automatically held to the correct canonical page, and you do not need to add any extra HTML code on your site.
Best Practices within Canonicalization
We’ve already protect few ways to set canonical tags on your website.

Now, allow take it a step further and look at some of the best practices you must follow when canonicalization your pages.
Use 1 Canonical Per Page
As mentioned fast, canonical tags act as advice, not strict commands. If you like Google to follow your canonical tag correctly, pls make sure that one page does not point to more than one canonical URL. Each page must have only one clear choice type.
The whole basis of a canonical tag is to show which page is the main version. If you add many canonical tags on a single page, Google will simply ignore them, and you lose all the benefits of using canonicals.
Be Consistent
Always be consistent with your canonical URLs. Like example, decide whether your URLs will involve a drag slash or not, and stick to that format across your site.
Recall that Google treats URLs as case sensitive. Make sure your canonical URLs are clear and in line so that crawlers understand exactly which page is the main one.
Use Absolute URLs
Google allows you to use both complete URLs (like www.domain.com/awesome-blog) and samilar URLs (like /awesome-blog) like canonical tags. However, as John Mueller has said, using absolute URLs is better because it removes any guesswork and offer more reliable results.
John Mueller also shared useful advice on Reddit: Anytime you depend on a computer script to interpret your instructions, it capable of reduce the success of your input. In SEO, it is important to be as clear as likely so search engines know your liking.
Don’t Use Noindex Tags and Canonical Tags on the Same Page
Avoid using a no-index tag and a canonical tag on the same page. John Mueller has again and again guide against this, in 2009, 2014, and 2018.
In a 2018 Reddit post, John explains that Google usually follows the canonical tag over the no-index, but this depends on how the crawler explains the page.
Since the two tags send conflicting instructions, it is best to not at all combine them. As John said: you must not pair a no-index with a rel=canonical pointing to an index able URL. Choose one, but not both.
Avoid Canonical Chains Like The Plague
This is maybe the most important rule in canonicalization: not at all set one page as a canonical URL and then point that page to another canonical URL. Performing carrying out so will confuse Google and other search engines, creating confusion around which page is the main version.
Canonical chains signal to search engines that multiple pages are equally the main version. To avoid this, make sure all canonicalized pages point directly to a single URL.
Always use double repeat when writing canonical tags.
Also Read: What are Seed Keywords in SEO? Examples & How to Find Them
The rel=”canonical” tag must follow this format according to web standards (RFC2616), whether it’s in HTML link attributes or HTTP headers.
Prioritize HTTPS over HTTP for Canonicals
In common, Google prefers to index pages that use HTTPS preferably than HTTP. However, if there are any issues with your HTTPS pages, Google power still choose to index the HTTP version instead.
The main situations that make Google prioritize HTTP over HTTPS are:
- An invalid SSL certificate.
- Pages with insecure content (other than images).
- Pages that redirect to or between an HTTP URL.
- Pages that have a canonical tag pointing to an HTTP page.
According to Google, you capable of take the following steps to ensure the HTTPS version is preferred:
- Redirect all HTTP pages to their HTTPS versions.
- Add canonical tags on HTTP pages pointing to the HTTPS version.
- Fix any SSL certificate warnings or security issues.
- Avoid redirects alike HTTPS to HTTP.
- Do not involve HTTP pages in your sitemap or hreflang tags.
Placement of Canonical Tags
Canonical tags good to be always a set in the <head> section of the page. Google will ignore any canonical tags placed within the <body>. It’s also move to include the canonical tag as quick as possible in the <head> section.
Don’t Canonicalize Category Pages to Featured Article / Product Pages
Google advises against setting a canonical alike a class page to a specific article or product, even if that item builds up a big part of the category. Category pages are usually dynamic and represent a collection of content, quite than start a copy of a single page.
Like example, study a category page like running shoes. If you set a canonical to the best selling running shoe, the category page listing all other shoes may be excluded alike search results.
Users do not always want the best selling product they may be looking like a different choice. So, with trying to canonicalize class pages to highlight a single popular product, many times to boost conversions or revenue, rarely works.
Don’t Canonicalize to First Instances of Paginated Pages
Google advises against setting the first page of a paging series as a canonical, because these pages are not study duplicate content on your website.
Pagination is used like product lists or post archives. Using canonical tags here capable of build it harder like users and search engines to way in different content, as few pages may be removed from the index.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is Rel Canonical Tag Code in HTML?
As told above that canonical tag is an HTML element that is used in the <head> section of your webpage. Once done; this helps to indicate the preferred version of a URL; for example
<link rel=”canonical” href=” https://digitalthinkerhelp.com/preferred-page/”>
What is Canonical URL Example?
As you know that, A canonical URL is the main type of a webpage are you like search engines to index. Example, if both https://example.com/helpor https://example.com/help?color=red exist, Are you choose the canonical URL to see main type.
Do Canonical Tags Affect SEO?
Yes! Canonical tags help mix ranking signals and stop duplicate content alike weakening your SEO. They show search engines which page to index, helping improve your clear in search results.
How to Find Canonical URL?
A canonical URL shows the main type of a webpage. You capable of find it by looking at the page’s HTML <link rel=”canonical”> tag, using SEO tools, or study your CMS settings. Canonical URLs help mix duplicate content signals and improve how search engines index and rank your pages.
Final Remarks
Like many parts of technical SEO, canonicalization capable of seem confusing at first. Now that you know it, you capable of use this knowledge to help Google’s bots index your website more effectively.
Also Read: What are Informational Keywords in SEO with Examples? Full Guide
If apply correctly, you must see results fairly quickly. Google usually indexes new canonical URLs within a few days, between in few cases it may take a couple of weeks, so improvements must become noticeable soon.


